A simple automatic motion-detection Digital Camera Circuit
When the sensor detects movement in a room it will take a burst of
10 photos with the digital camera. Each photo is taken at 0.5sec
interval. After the 10 photos, the camera waits 3 seconds for further
movement and if it is detected, the process is repeated until 80
photos are taken.
The photos can then be downloaded to your PC (via the USB
connection on the board) for viewing.
 more
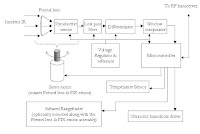
moreThe Directional Infrared Detector Module Circuit (DIRM)
Figure shows a block diagram of the DIRM. A Fresnel lens
captures the incident IR and focuses it towards the
pyroelectric sensor increasing the sensitivity of the sensor
and improving its directional response. The resultant signal
passes through a low pass filter, which removes any high
frequency noise generated by mechanical vibration. The
output of the filter is then fed into a differentiator, which
produces an output voltage proportional to the rate of
change of the incident IR. The frequency response of this
differentiator is also rolled off at high frequencies, further
reducing the effects of undesired signals. The window
comparator produces a logic output whenever the rate of
change of incident IR exceeds a given set point.
An 8-bit PIC16F84 microcontroller processes the logic
signals and controls the rotating platform and reports
information to the team leader.
more
PIR DETECTOR USING ST7FLITE05 MICROCONTROLLER
A PIR detector can be made easily with ST7FLITE05 using the
circuit shown in Figure. The sensor interfacing circuit (shown on
the left side of the microcontroller in Figure ) can be divided
into the following modules:
1.Transistor circuit used as an amplifier.
2.Transistor biasing controlled through the microcontroller.
3. Software-controlled transistor output.

more pdf
Infrared, Alarm, and PIC Microcontroller
OBJECTIVES:
• Get familiar with an infrared emitter diode and receiver.
• Create an obstacle detector with an infrared emitter and receiver.
• Learn about PIC microcontroller and programming a PIC microcontroller.
• Write a PIC program and build the circuit of a household alarm system.

more pdf
Ultra-low Power Motion Detection using the MSP430F2013
A system capable of detecting motion using a dual element PIR
sensor is shown in Figure 1 using the MSP430F2013
microcontroller. Using the integrated 16-bit Sigma-Delta
analog-todigital converter and built-in front-end PGA (SD16_A),
the MSP430F2013 provides all the required elements for interfacing
to the PIR sensor in a small footprint. With integrated analog
and a 16MHz, 16-bit RISC CPU, the MSP430F2013 offer a great
deal of processing performance in a small package and at a low cost.